Слайды презентации
Слайд 2
Big companies employing a large
workforce have complex internal
structures,
with separate specialist
department in charge of diferent
functions.
Слайд 3
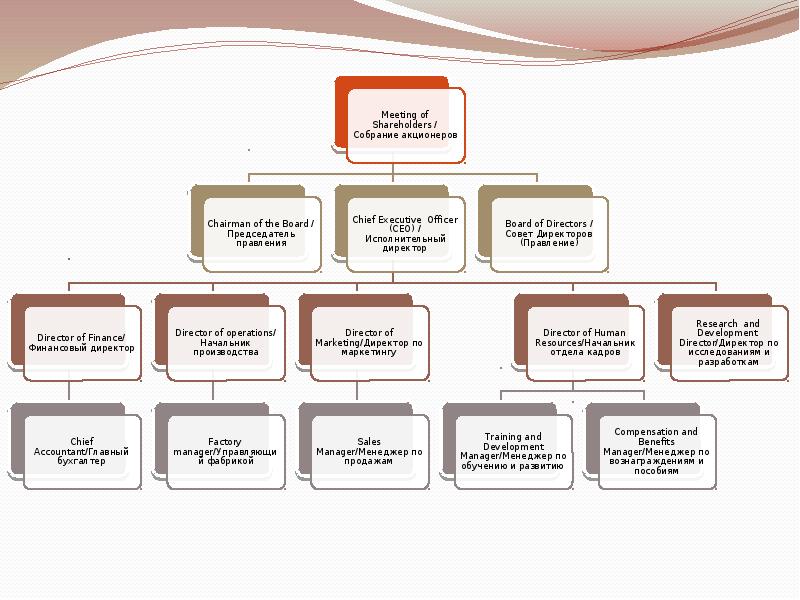
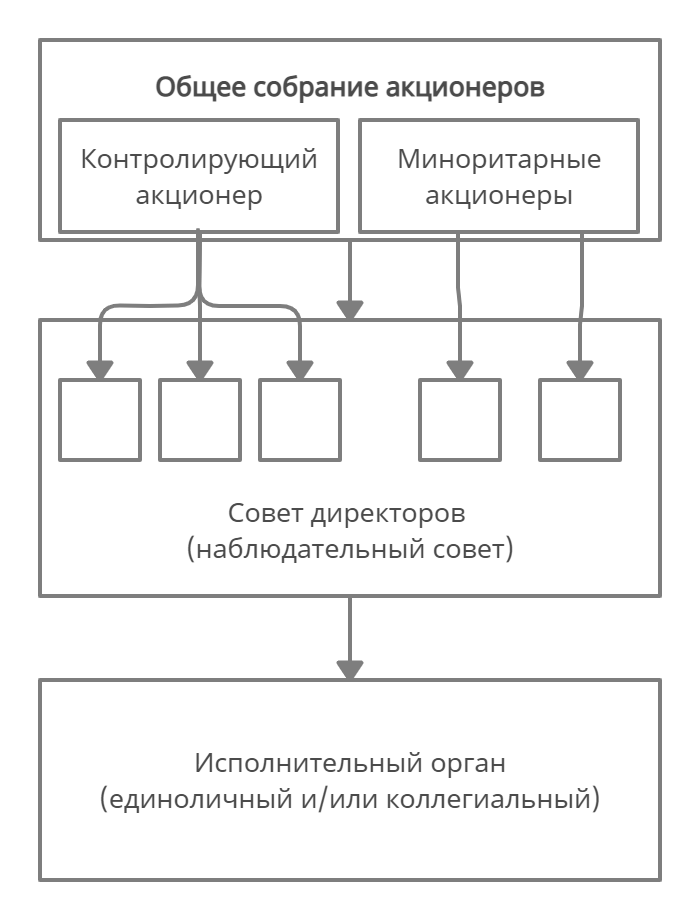
Meeting of
Shareholders /
Собрание акционеров
Chairman of the
Board /
Председатель
правления Chief Executive Ofcer
(CEO) /
Исполнительный
директор
Director
of Finance/
Финансовый
директор
Chief
Accountant/Главный
бухгалтер Director of operations/
Начальник
производства
Factory
manager/Управляющи
й фабрикой Director of
Marketing/Директор
по маркетингу
Sales
Manager/Менеджер
по продажам Director of Human
Resources/Начальник
отдела кадров
Training and
Development
Manager/Менеджер
по обучению и
развитию Compensation and
Benefits
Manager/Менеджер
по вознаграждениям
и пособиям Research and
Development
Director/Директор по
исследованиям и
разработкамBoard of Directors /
Совет Директоров
(Правление)
Слайд 4
Meeting of Shareholders
•
The General Meeting of
Shareholders is the Company’s
supreme governing body.
Shareholders have the right to
participate in management of
the Company afairs, taking
decisions in
the key areas of
Company business at the
meetings of shareholders.•
An Annual General Meeting of
Shareholders (AGM) is organised
within six months of the end of
the financial year. Further
Extraordinary Meetings of
Shareholders (EGM), may be
held at the request of the
Executive or Supervisory Boards
Слайд 5
Board of Directors
Governing body of a
company. Its members are
elected
by the stockholders
of the company
Duties :
set
the company’s policy, objectives
, and overall direction;
name members of
the advisory, executive, fnance,
and other committees;
hire, monitor, evaluate and fre
the Managing Director and
Seniors executives;
determine and pay the
dividend;
Issue additional shares
setting the salaries and
compensation of company
management;
Слайд 6
Chairman of the Board (COB)
The most powerful
member on the board
of
directors who provides
leadership to the firm’s
ofcers and
executives. The
COB ensures that the firm’s
duties to shareholders are
being fulfilled by acting as a
link between the board and
upper management.
Слайд 7
Chief Executive Ofcer (CEO)
The highest ranking executive
in a
company
Responsibilities:
developing and
implementing high-level
strategies
making
major corporate
decisions
acting as the main point
of
communication between
the board of directors and
the corporate operations
Слайд 9
Departments
Accounting
Human Resources
Marketing
Production
Sales
Works
IT
Logistics
Research and Development
Слайд 10
Accounting departments examine and analyze
money within the company.
Responsibilities
:
—
payroll
— cash payments (disbursements)
—
procurement and inventory
— cash collections
— property accounting
Слайд 11
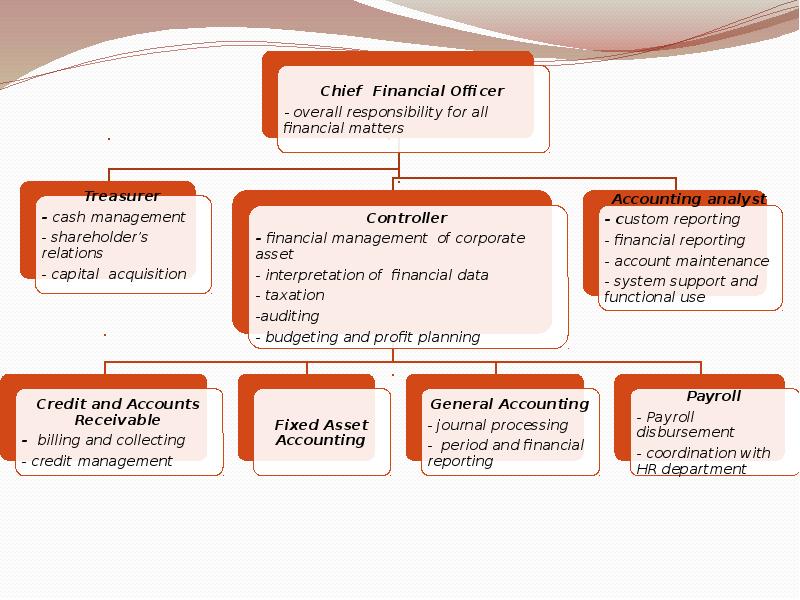
Chief Financial Ofcer
— overall responsibility for all
fnancial matters
Treasurer
— cash
management
— shareholder’s
relations
— capital acquisition Controller
— fnancial management of
corporate
asset
— interpretation of fnancial data
— taxation
-auditing
— budgeting and
proft planning
Credit and Accounts
Receivable
— billing and collecting
— credit management Fixed Asset
Accounting General Accounting
— journal processing
— period and fnancial
reporting Payroll
— Payroll
disbursement
— coordination with
HR departmentAccounting analyst
— c ustom reporting
— fnancial reporting
— account maintenance
— system support and
functional use
Слайд 12
Human resources hires, fires, administrates,
motivates and provides services
for employees.
Слайд 13
Human Resource Management (HRM, HR) is the
management of an
organization’s employees.
While human resource management is sometimes
referred
to as a «soft» management skill, efective
practice within an
organization requires a strategic
focus to ensure that people resources can facilitate
the achievement of organizational goals. Efective
human resource management also contains an
element of risk management for an organization
which, as a minimum, ensures legislative
compliance. Human Resource Management
Слайд 14
Marketing and sales deal with
customers and sell the company’s
products.
Слайд 15
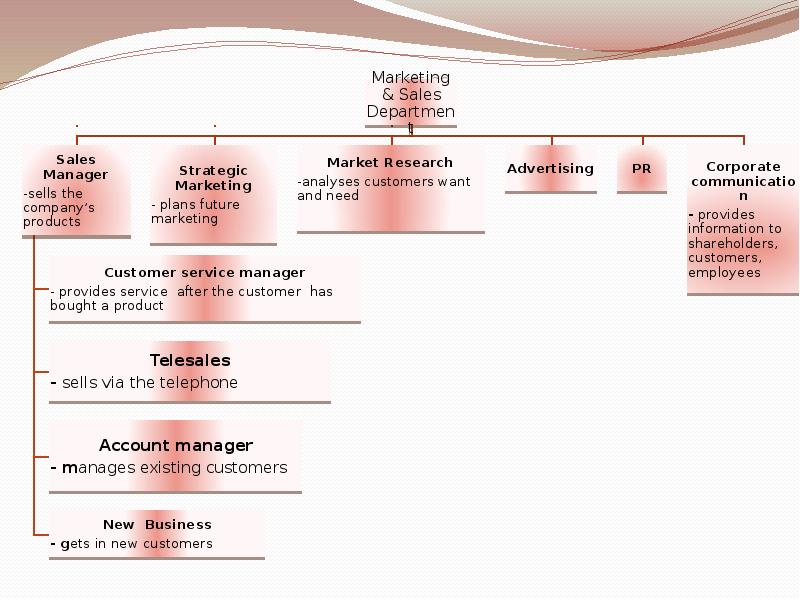
Marketing
& Sales
Departmen
t
Sales
Manager
-sells the
company’s
products
Customer service manager
—
provides service after the customer has
bought a product
Telesales
—
sells via the telephone
Account manager
— m anages existing customers
New Business
—
g ets in new customers Strategic
Marketing
— plans future
marketing Market Research
-analyses customers want
and need Advertising PR Corporate
communicatio
n
— provides
information to
shareholders,
customers,
employees
`
;
^
R
^
S
^
^
! »
Чтобы скачать презентацию — поделитесь ей с друзьями с помощью
социальных кнопок.
- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Страхование
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Содержание
-
1.
Companies -
2.
plan Types of companies Company structure -
3.
Types of companies Company – is a -
5.
Company structure In general a company can -
6.
Apple -
7.
Plan About Apple Products Reasons for Apple’s success mission -
8.
About Apple Apple is an American multinational technology company headquartered -
9.
Products Hardware products include the iPhone smartphone, the iPad tablet computer, the Mac personal computer, the iPod portable media player, the Apple Watch smartwatch. -
10.
Reasons for Apple’s success Apple have a -
11.
mission «To provide students, teachers, creative professionals
plan Types of companies Company structure
Слайд 2plan
Types of companies
Company structure

Слайд 3Types of companies
Company – is a business organization that makes or
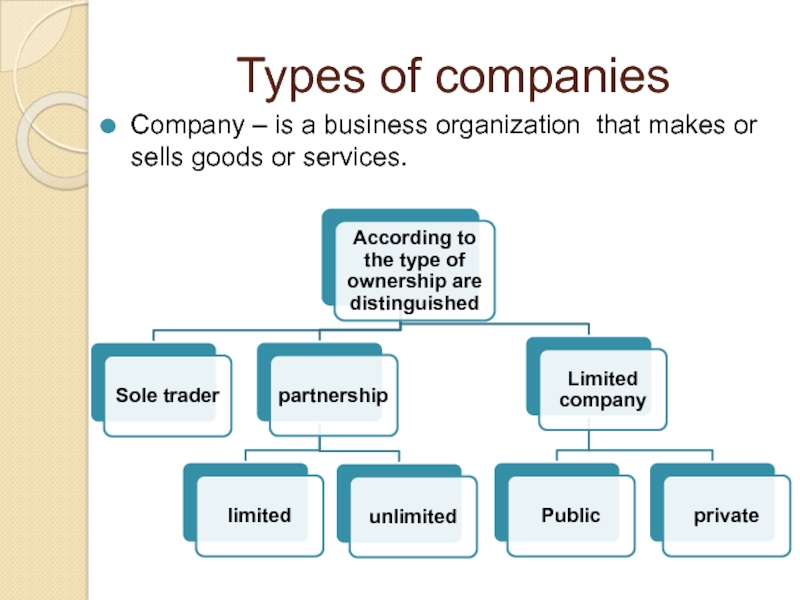
Слайд 5Company structure
In general a company can be:
Flat
Hierarchical
Reasons for choosing the company
structure:
company business;
commitments of the top management;
company size;
number of full-time and part-time workers (freelancers);
office size;
company financial state

Слайд 7Plan
About Apple
Products
Reasons for Apple’s success
mission

Слайд 8About Apple
Apple is an American multinational technology company headquartered in Cupertino, California, that designs, develops, and
sells consumer electronics, computer software, and online services. Apple became the first U.S. company to be valued at over US$700 billion. The company employs 115,000 permanent full-time employees as of July 2015 and maintains 478 retail stores in seventeen countries as of March 2016.

Слайд 9Products
Hardware products include the iPhone smartphone, the iPad tablet computer, the Mac personal computer, the iPod portable media player, the Apple

Слайд 10Reasons for Apple’s success
Apple have a very talented team of young
designers. Our distribution system is first class. And we’re very creative when advertising and promoting our products.

Слайд 11mission
«To provide students, teachers, creative professionals around the world the best
personal computers through the use of innovative solutions»

Presentation on theme: «COMPANY STRUCTURE.»— Presentation transcript:
1
COMPANY STRUCTURE
2
1.A disadvantage of … is that …
3
People involved in corporate structure
shareholders management workforce
4
WORKFORCE senior staff ≠ junior staff
employees /staff/personnel senior staff ≠ junior staff higher-positioned ≠ lower-positioned superiors ≠ subordinates Mary is Kate’s superior. Kate is Mary’s subordinate.
5
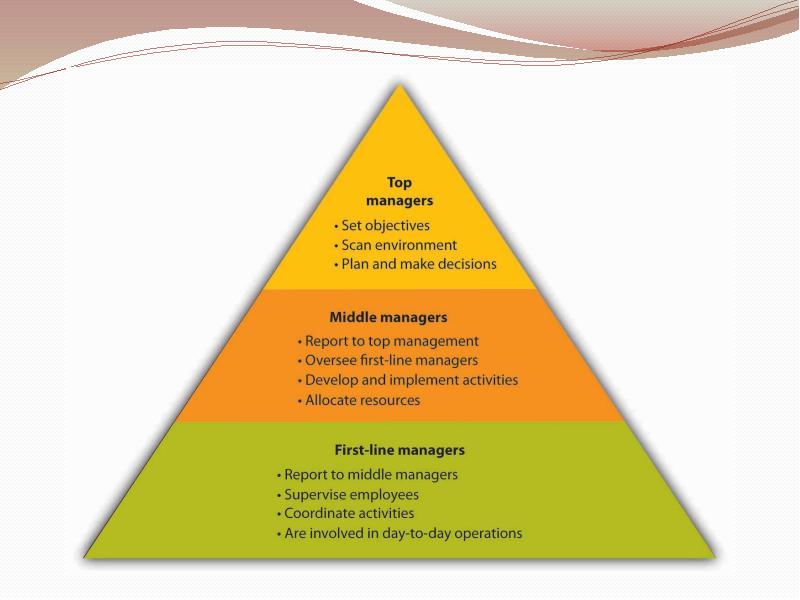
MANAGEMENT Top management Senior management Middle management
Lower management
6
Traditional hierarchies or more flexible systems?
Division of responsibilities Chain of command Line authority Flattening hierarchies Accountability Delegating responsibilities Empowerment
7
Types of company structure MK: pp.22-23
Hierarchical (pyramidal) Functional Matrix Team Flattening hierarchies? Flat organisation? Advantages/disadvantages of each type?
8
Assignment: COMPANY STRUCTURE (MK, pp.22-23)
HIER. FUNCT. MATRIX TEAM advantages disadvantages
9
Division of responsibilities
What are you responsible for? What are you in charge of? What are your responsibilities?
10
Chain of command and line authority
Who is your superior? Who do you report to? Who are you responsible to? Who are you accountable to? Who are you subordinated to? Who do you receive instructions from?
11
Chain of command and line authority
Who can appoint YOU? promote remove dismiss Who reports TO YOU? Who is accountable to you?
12
For example, …
13
ORGANISATION UNITS DEPARTMENTS DIVISIONS SECTORS SECTIONS
BUSINESS UNITS ARMS
14
ORGANISATION UNITS The company consists … is composed … is divided …
is made … contains … …departments/division/sectors/ sections/business units/ arms…
15
ORGANISATION UNITS The company consists OF… is composed OF…
is divided INTO… is made UP OF… contains … …departments/division/sectors/ sections/business units/ arms…
16
DIVISION vs DEPARTMENT
Usually product-based (or market-based) e.g. Food Division Cosmetics Division Automotive Division Plastics Division European Division Asian Division Usually function-based e.g. Production Department Finance Department Purchasing Department Marketing Department Sales Department HR Department PR Department R&D Department IT Department ICT Department
17
DIVISION vs DEPARTMENT
Usually product-based (or market-based) e.g. Food Division Cosmetics Division Automotive Division Plastics Division European Division Asian Division, … Usually function-based e.g. Production D. Finance D. Purchasing D. Marketing D. Sales D. Human Resources (HR) D. Public Relations (PR) D. Research & Development (R&D) Information Technology (IT) D.
18
Make sentences.Use the following: -consist of, contain, report to, -be accountable/responsible/subordinated to, -composed of/divided into/made up of
19
2.The Production Deparment … the Cosmetics and the Food Division.
Make sentences.Use the following: -consist of, contain, report to, -be accountable/responsible/subordinated to, -composed of/divided into/made up of 1.The company … four …. 2.The Production Deparment … the Cosmetics and the Food Division. 3. Department managers …. the Managing Director. 4. The Cosmetics and the Food division managers … the Production Manager.
20
Help needed? 1.The company CONSISTS… four DEPARTMENTS.
2.The Production Deparment IS DIVIDED .. the Cosmetics and the Food Division. 3. Department managers REPORT …. the Managing Director. 4. The Cosmetics and the Food division managers ARE ACCOUNTABLE… the Production Manager.
21
Key: 1.The company CONSISTS OF four DEPARTMENTS.
2.The Production Deparment IS DIVIDED INTO the Cosmetics and the Food Division. 3. Department managers REPORT TO the Managing Director. 4. The Cosmetics and the Food division managers ARE ACCOUNTABLE TO the Production Manager. Use the other expressions from Slide 17 to replace the phrases above.
22
MANAGEMENT AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
The Board of Directors The Chairman Executive directors (inside directors) Non-executive directors (outside directors)
23
The management team CEO – Chief Executive Officer
(the company’s president) or Managing Director (MD) CFO — Chief Finance Officer (senior vice-president) COO – Chief Operations Officer …
24
Croatia The Supervisory Board The Management Board or
The Board of Directors
25
Wikinomics and the future of companies (MK, p.21)
Title? Synonym for ‘cooperate’? Opposite to ‘outsourcing’? A word linking wikinomics and outsourcing?
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1
Описание слайда:
Organisation Structure
Harry Kogetsidis
School of Business
Слайд 2
Описание слайда:
Lecture’s topics
What is organisation structure?
What are the basic elements of organisation structure?
What are the basic types of organisation structure?
Слайд 3
Описание слайда:
Organisation Structure
Organisation structure describes the way work is
divided, supervised and coordinated.
Слайд 4
Описание слайда:
Organisation Charts
Organisation structure is often represented by an
organisation chart – i.e. a chart showing the main
departments and work positions in the organisation
and the reporting relations between them.
Слайд 5
Описание слайда:
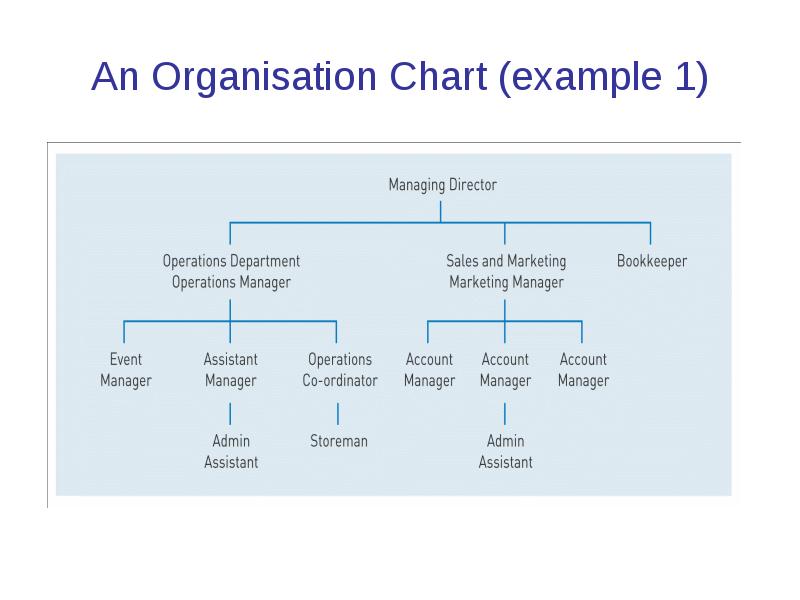
An Organisation Chart (example 1)
Слайд 6
Описание слайда:
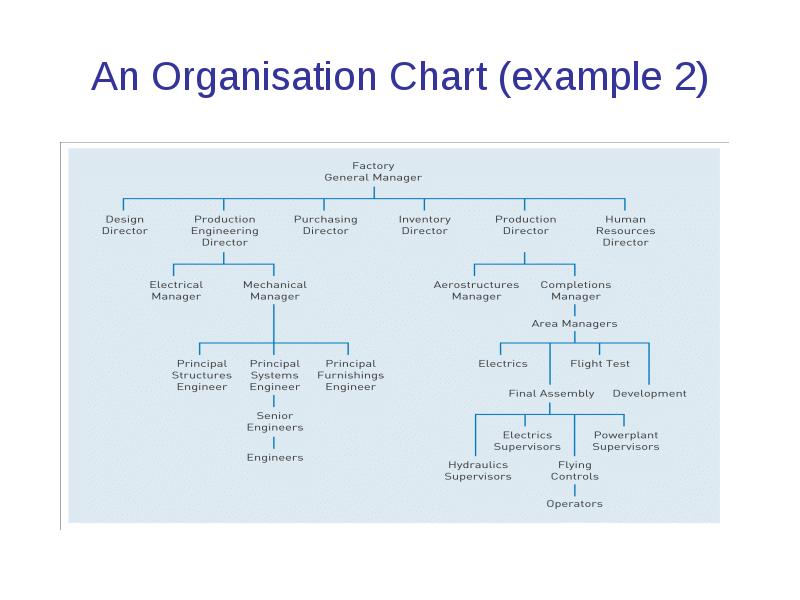
An Organisation Chart (example 2)
Слайд 7
Описание слайда:
Types of structure
Formal structure:
The official structure of the organisation.
The official guidelines, documents or procedures setting out how the organisation’s activities are divided, supervised and coordinated.
Слайд 8
Описание слайда:
Types of structure
Informal structure:
The unofficial, but often critical, working relationships between organisational members.
If this could be drawn, it would show who talks to and interacts regularly with whom regardless of their formal titles and relationships.
Слайд 9
Описание слайда:
The Basic Elements of Structure
1. Work specialisation
2. Chain of command
3. Span of control
4. Centralisation vs Decentralisation
5. Departmentalisation
Слайд 10
Описание слайда:
Work Specialisation
a job is broken down into a number of steps and each step is completed by a separate individual
different employees have different skills
need to make efficient use of the diversity of skills that employees have
Слайд 11
Описание слайда:
Negative results of work specialisation
Слайд 12
Описание слайда:
Chain of Command
The continuous chain of authority that extends
from the highest levels in an organisation to the
lowest levels and clarifies who reports to whom.
Слайд 13
Описание слайда:
Chain of Command
Early management writers believed that each
employee should report to only one manager –
a term called unity of command.
Слайд 14
Описание слайда:
Chain of Command
Some concepts closely related to chain of command:
Authority
Responsibility
Accountability
Delegation
Слайд 15
Описание слайда:
Authority
The right that a person in a specified role has to make
decisions, allocate resources or give instructions.
If managers attempt to give instructions beyond their
area of formal authority, they are likely to meet
resistance.
Слайд 16
Описание слайда:
Responsibility
An employee’s duty to perform assigned activities
and to meet the expectations associated with a
task.
Слайд 17
Описание слайда:
Accountability
Employees with formal authority over an area are
required to report on their work to those above
them in the chain of command.
Слайд 18
Описание слайда:
Delegation
Managers giving people who are below them in
the chain of command the authority to undertake
specific activities or decisions.
Слайд 19
Описание слайда:
Authority vs Power
Authority
Power
Слайд 20
Описание слайда:
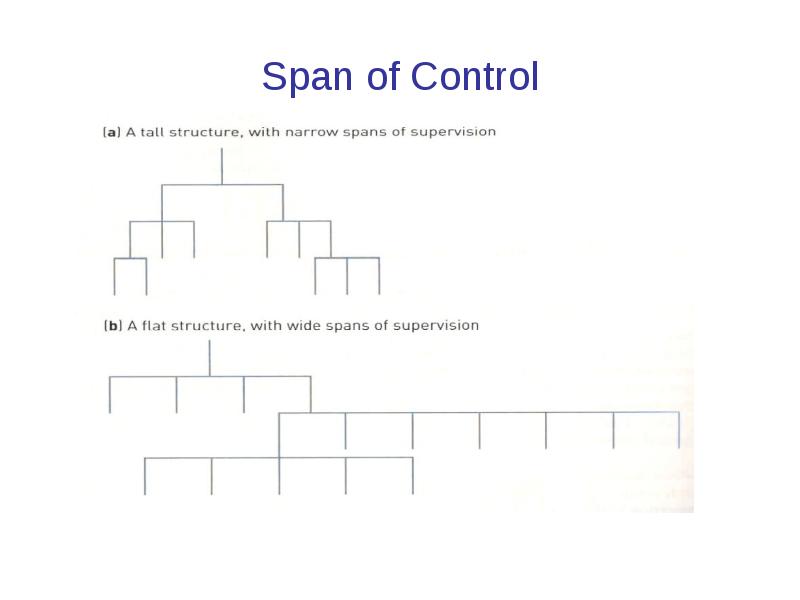
Span of Control
The number of persons (subordinates) directly
reporting to a manager.
The right number must be found in order for these people to be managed effectively and efficiently.
Слайд 21
Описание слайда:
Span of Control
The level of direct supervision an employee needs
decreases with the level of experience they have and
training they receive.
Слайд 22
Описание слайда:
Span of Control
Слайд 23
Описание слайда:
Centralisation vs Decentralisation
Centralised organisations: decisions are made
by a few people at the centre of the organisation.
Decentralised organisations: decisions are pushed
down to the level closest to where the problem is.
Слайд 24
Описание слайда:
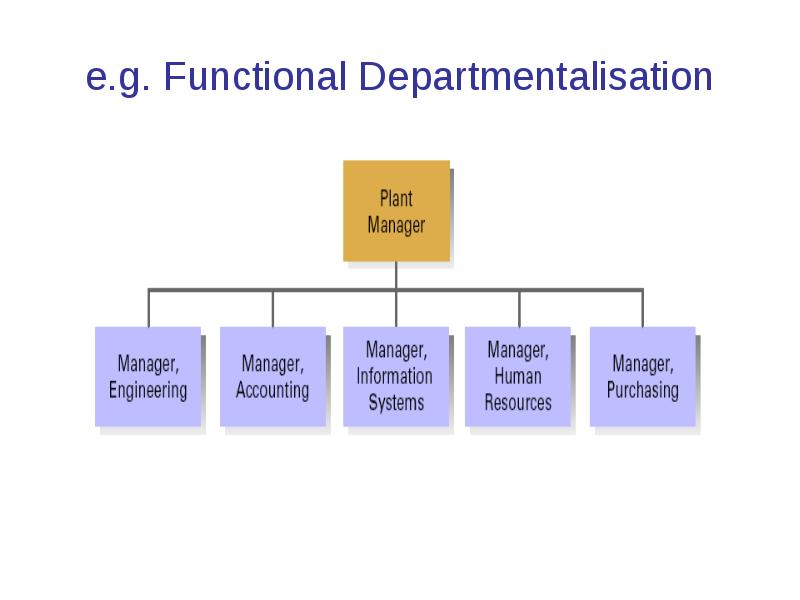
Departmentalisation
refers to how the various activities of the organisation are grouped together into units
a manager is in charge of each unit
Слайд 25
Описание слайда:
e.g. Functional Departmentalisation
Слайд 26
Описание слайда:
Types of Structure
Mechanistic structure
Organic structure
(Burns & Stalker, 1961)
Слайд 27
Описание слайда:
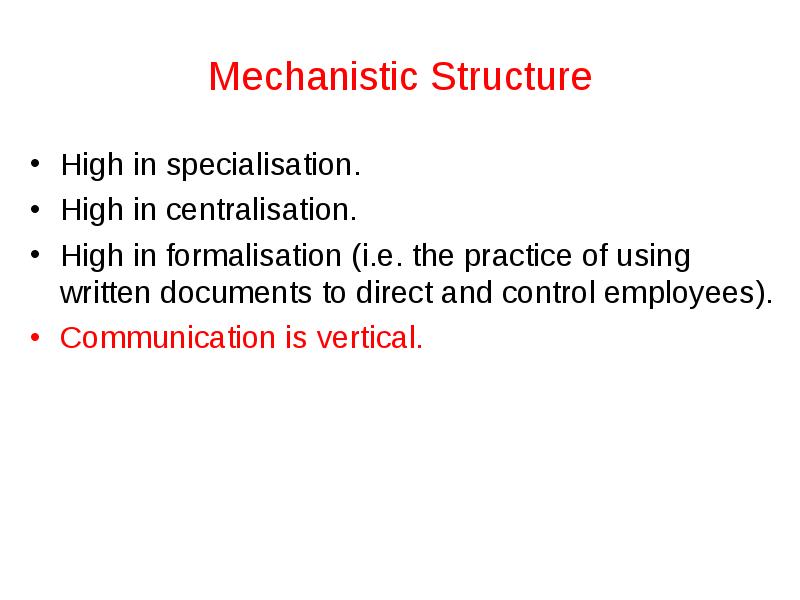
Mechanistic Structure
High in specialisation.
High in centralisation.
High in formalisation (i.e. the practice of using written documents to direct and control employees).
Communication is vertical.
Слайд 28
Описание слайда:
Organic Structure
Knowledge is widely spread.
There are few prescriptive job descriptions and rules and regulations are kept to a minimum.
Cross-functional team work is encouraged.
Communication is horizontal.
Слайд 29
Описание слайда:
Types of structure
One of the these two types of structure is frequently
called a ‘bureaucracy’. Which one is it?
Слайд 30
Описание слайда:
Types of structure
Mechanistic structure:
Rigid and stable.
Organic structure:
Flexible and highly adaptive.
Слайд 31
Описание слайда:
Types of structure
Mechanistic structure:
Best at simple and repetitive tasks.
Organic structure:
More effective at complex and unique tasks.
Слайд 32
Описание слайда:
Types of structure
Mechanistic structures are most effective in stable
environments.
Organic structures are most effective in dynamic
and uncertain environments.
Слайд 33
Описание слайда:
Types of structure
Organisations could use a combination of the
two types.
e.g. finance department – mechanistic
advertising department – organic
Слайд 34
Описание слайда:
Group Work
Produce an organisation chart that, to the best of your
knowledge, represents the structure of the University of
Nicosia. Use an exclamation mark for departments or
units that you know with certainty that they exist (such
as academic affairs or finance). Use a question mark for
those that you think might be part of this organisation.
You should produce separate charts for the academic
and administrative structures of the institution.
Вы можете ознакомиться и скачать презентацию на
тему Company structure .
Доклад-сообщение содержит 16 слайдов.
Презентации для любого класса можно скачать бесплатно.
Если материал и наш сайт презентаций Mypresentation Вам понравились – поделитесь
им с друзьями с помощью социальных кнопок и добавьте в закладки в своем
браузере.
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1
Описание слайда:
Company structure
Слайд 2
Слайд 3
Слайд 4
Описание слайда:
Meeting of Shareholders
Слайд 5
Описание слайда:
Board of Directors
Слайд 6
Описание слайда:
Chairman of the Board (COB)
Слайд 7
Описание слайда:
Chief Executive Officer (CEO)
Слайд 8
Слайд 9
Описание слайда:
Departments
Accounting
Human Resources
Marketing
Production
Sales
Works
IT
Logistics
Research and Development
Слайд 10
Слайд 11
Слайд 12
Слайд 13
Описание слайда:
Human Resource Management (HRM, HR) is the management of an organization’s employees. While human resource management is sometimes referred to as a «soft» management skill, effective practice within an organization requires a strategic focus to ensure that people resources can facilitate the achievement of organizational goals. Effective human resource management also contains an element of risk management for an organization which, as a minimum, ensures legislative compliance.
Human Resource Management (HRM, HR) is the management of an organization’s employees. While human resource management is sometimes referred to as a «soft» management skill, effective practice within an organization requires a strategic focus to ensure that people resources can facilitate the achievement of organizational goals. Effective human resource management also contains an element of risk management for an organization which, as a minimum, ensures legislative compliance.
Слайд 14
Слайд 15
Слайд 16
Описание слайда:
THANK YOU
THANK YOU
Chapter One Company Structure • Organizational structure specifies the firm’s formal reporting relationships, procedures, controls, authority and decision-making processes.
Compare & Contrast • Characteristics • Advantages • Disadvantages • • Simple Functional Multidivisional Matrix
Organizational Circle: Moving back to flat • The flat structure is common in enterprenerial start-ups, university spin offs or small companies in general. As the company grows, however, it becomes more complex and hierarchical, which leads to an expanded structure, with more levels and departments. ØStarbucks ØProcter & Gamble ØToyota ØUnilever
Team Structure Ø One of the newest organizational structures developed in the 20 th century is team. In small businesses, the team structure can define the entire organization. • formed at the beginning of product development process and continued throughout implementation • speeds innovation and customer responsiveness • stronger in highly dynamic industries ü Whole Foods Market ü Xerox ü Motorola ü Daimler. Chrysler
Network Structure Ø Another modern structure is network. While business giants risk becoming too clumsy to proact, act and react efficiently, the new network organisations contract out any business function, that can be done better or more cheaply. • Core group of experts manages the outsourcing process closely • This forms a hub & spoke type of organization consisting of many contracts • Could create a control problem with contract organizations Ø H&M
.
Boundaryless structure Ø The most radical concept in today’s organisational design is the concept of ‘boundarylessness’, which seeks to overcome traditional boundaries between layers of management (vertical), functional areas (horizontal), as well as geographic boundaries. Some claim the boundaryless structure is a combination of team and network structures, with the addition of temporariness. ü Ikea
Virtual Structure Ø A special form of boundaryless organisation is virtual. It works in a network of external alliances, using the Internet. This means while the core of the organisation can be small but still the company can operate globally be a market leader in its niche. According to Anderson, because of the unlimited shelf space of the Web, the cost of creahing niche goods is falling dramatically. Although none sell in huge numbers, there are so many niche products that collectively they make a significant profit, and that is what made highly innovative Amazon. com so successful. ü Amazon. com
Organizational Structure Slides 14 -23 Extensive Reading Material • Building blocks of organizational structure are: – Differentiation — allocation of people to tasks • vertical — distribution of decision-making (levels) • horizontal — distribution of functions – Integration — coordination between people or functions or divisions or companies. – Differentiation + Integration = Bureaucratic Costs (time spent in meetings, # of managers)
• Vertical differentiation: • Reporting relationships that link people, tasks and functions – appropriate # of levels – appropriate span of control – determines if a structure is flat or tall • Tall structures – impede communication & coordination – raise bureaucratic costs – distort information (intentional & non-intentional) – decreases motivation – too many middle managers (structure begets structure)
• Vertical differentiation: – Centralization: – easier coordination of activities – decisions fit organizational strategy – speedy decision making – Decentralization: – reduces overload for TMT (can focus on strategy) – ee motivation & accountability increase – fewer managers are needed — flatter structure
Organizational Structure • Horizontal differentiation – The degree to which you separate tasks or skills in the organization (specialization or functionalization). • Many organizational forms: Functional Mechanistic Multi-Divisional Matrix Team Network ? Organic
Mechanistic vs. Organic Feature Task Definition Mechanistic Rigid and highly specialized Coordination and Rules and directives vertically Control imposed Communication Knowledge Flexible and less narrowly defined Mutual adjustment, common culture Vertical and horizontal Centralized Dispersed Commitment and To immediate supervisor Loyalty Environmental Context Organic Stable with low technological uncertainty To the organization and its goals Unstable with significant technological uncertainty and ambiguity
• Common success criteria for organizational structures are: – Decentralized reporting – Flat hierarchy – High transient speed – High transparency – Permanent monitoring – Rapid response – Shared reliability
Sony Group Structure 1. New Group Headquarters to Function as Hub for Group Strategy 1) 2) 3) a. b. Global Hub (GH) as Sony Group HQ Management Platform for Global Staff Support Electronics HQ for Related Businesses Reorganizing Network Companies (NCs) for the broadband era Introducing horizontal platform concept • 2. Electronics Businesses Strengthened: Pursuing a Ubiquitous Value Network 1) Developing Hardware for the Ubiquitous Value Network 2) Constructing a Network Platform • Establishing a center to promote a common network platform for the entire group 3) Strengthening Internet/Communication Services 4) Creating New Forms of Entertainment to Integrate Hardware, Content and Services 3. Network-Based Content Distribution: Key for Entertainment Business and Financial Services 1)Broadband Entertainment Content a. Digital distribution of films b. Digital distribution of music 2) Development of Network Compatible Financial Services a. Establishing a net bank b. Electronic money service
Part II Reading: Time for the big small company
– big small company – … the dream is to marry the control of an established company with the responsiveness of a start-up. – Operating processes define how a company produces, sells, distributes and supports its products and services. (para. 2) – Management processes in such companies are also hampered by the time it takes to recognize that change is needed. (para. 3) – IT co-ordinates complex fast-cycle operating processes and, more importantly, gives decisionmakers quick access to detailed, real-time information about operations and market performance. (para. 5)
– Management processes in such companies are also hampered by the time it takes to recognize that change is needed. (para. 3) – IT co-ordinates complex fast-cycle operating processes and, more importantly, gives decision -makers quick access to detailed, real-time information about operations and market performance. (para. 5)
• Questions – What are the advantages and disadvantages of each company structure?
Hierarchical structure • Advantages – High level of control • Disadvantages – Workers lack the authority and motivation to improve process. – Management’s response time is slow. – Only suitable for stable business environment.
Entrepreneurial structure • Advantages – Totally centralized authority and direct control between owner and employees ensure responsiveness to external changes. • Disadvantages – Only suitable for small companies
Information age structure • Advantages – Allows speed of response within a large complex structure. Retains control but gives quick access to information. – Employees can constantly refine their actions and strategies. – Organization control is dynamic. • Disadvantages – Although IT makes all these advantages possible, it cannot motivate people to use the information they have.
Vocabulary • • • Hierarchical company • Channels of communication • Nimble • Responsiveness • Budgeting • Standardization • Hamper • Entrepreneurial organization • Flexibility • Real-time • Refine • Agility • 金字塔结构公司 沟通渠道 灵活的 快速应变 预算 规范化 妨碍 创业机构 灵活性 实时的 优化 敏捷
Questions for next calss • Why do companies want to go public? • Why do ordinary people buy stocks and securities? • What are indicators of stock market?
1. COMPANY STRUCTURE
Elizaveta Kurilo
2. Types of organizational structures
• Functional structure (traditional chain of
command)
• Product lines (divisions)
• Geographic structure (country managers)
• Matrix structure (project teams)
3. Restructuring strategies
Delayering process
Centralisation
Outsourcing
Downsizing (layoff)
Starburst
Business Process Reengineering
Virtualization
4. Downsizing
This restructuring strategy is about reducing the
manpower to keep employee costs under
control.
Downsizing is not always a result of business
losses; it may be needed even in cases of
takeovers or acquisitions and mergers.
5. British airways
is the largest airline of UK
supported by 50,000 employees, a level of
staffing was oversized.
At the time of the oil crises (1970s) its huge
staff resulted in massive financial losses.
The company soon developed a reputation for
terrible service as a result.
The new chairperson Lord King decided to
restructure the entire organization by reducing
its workforce from 59,000 to 39,000
6.
What is important is that before King began
announcing layoffs, he explained his reasons
for the restructuring to the entire company to
prepare them for the upcoming change.
Otherwise the company could have experienced
negative press around all the layoffs.
7. Starburst
This restructuring strategy involves breaking
a company into smaller independent
business units for increasing flexibility and
productivity.
8. Google splits up under the Alphabet umbrella
Google as a company grew monstrously
diverse.
So Google was broken up into its constituent
parts, making each one its own company, with
all of them owned by a new umbrella
corporation called Alphabet.
9.
10. Business process reengineering
• This type of restructuring is carried out for
making operational improvements. It begins
with identifying how things are being done
currently and then it moves on to reengineering the tasks to improve productivity.
• Business process re-engineering usually results
in changing roles.
• It may lead to layoffs, and can also create new
employment opportunities.
11.
When Ford Motor was trying to reduce its
cost, it found that the process at its financial
department needed to be re-engineered.
75% of the staff from this department was laid
off
The reengineering helped in simplifying the
controls and maintaining the financial
information more accurately
12.
The strategy involves pushing employees
outside the office to places where they are
more needed like at the client’s site.
It also involves upgrading to technology,
which allows virtual offices to be set up.
For example, the ATMs offered by banks are
their virtual units.
13.
Large organizations tend to follow routine,
gain “organizational fat” and play the
same game that made them successful in
the past